How Does Melamine Plywood Support Sustainable Building Practices?
2025-04-29
In today's environmentally conscious construction landscape, building materials that combine functionality with ecological responsibility are increasingly sought after. Melamine Plywood stands out as a versatile solution that significantly contributes to sustainable building practices. This innovative material, consisting of a plywood core covered with melamine-impregnated paper, offers remarkable durability, design flexibility, and environmental benefits that align perfectly with green building objectives. Through reduced waste, enhanced energy efficiency, and minimal chemical emissions, Melamine Plywood enables architects, builders, and homeowners to create spaces that are both beautiful and environmentally responsible without compromising on quality or aesthetics.
Environmental Benefits of Melamine Plywood in Construction
Resource Efficiency and Waste Reduction
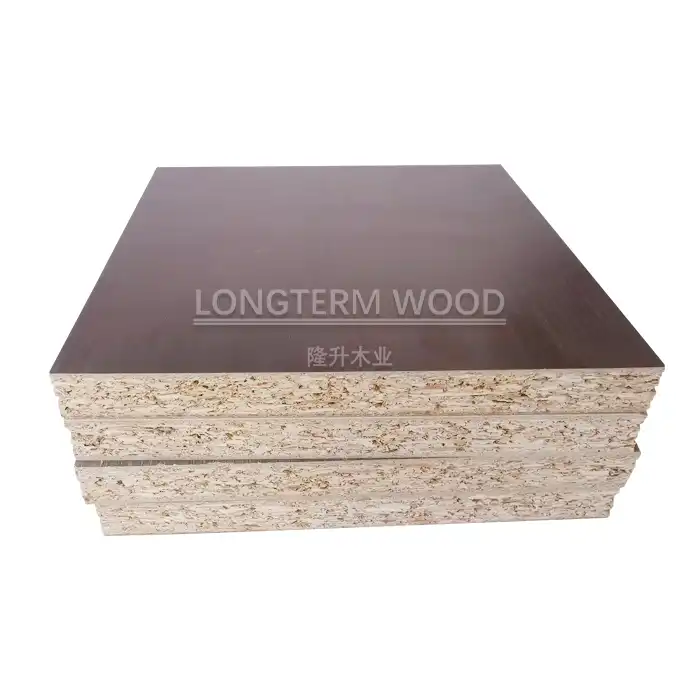
Melamine Plywood represents a significant advancement in resource-efficient building materials, addressing multiple sustainability concerns in modern construction. Unlike solid hardwood products that require harvesting mature trees, Melamine Plywood utilizes fast-growing wood species and manufacturing processes that maximize timber yield. The core structure consists of multiple thin layers of wood veneer or other wood-based materials bonded together, allowing manufacturers to use smaller diameter trees and even wood residues that might otherwise be discarded. This approach dramatically increases the usable wood fiber obtained from each harvested tree, helping to conserve forest resources while maintaining structural integrity.
Furthermore, the production of Melamine Plywood incorporates waste reduction strategies throughout the manufacturing cycle. Wood scraps generated during processing are typically repurposed as biofuel for factory operations or recycled into other wood-based products, creating a closed-loop manufacturing system. The application of melamine resin to the plywood surface extends this efficiency by providing a protective finish that eliminates the need for additional treatments or coatings once installed. This integration of finishing and structural elements reduces material consumption and simplifies construction processes, decreasing the overall environmental footprint of building projects. By choosing Melamine Plywood for cabinetry, furniture, and interior applications, builders can significantly minimize construction waste while maintaining high-quality standards and aesthetic appeal.
Longevity and Reduced Replacement Cycles
One of the most significant yet often overlooked aspects of sustainability in building materials is longevity—products that last longer require fewer replacements, conserving resources and reducing environmental impact over time. Melamine Plywood excels in this critical dimension through its exceptional durability characteristics. The melamine surface creates a protective shield against daily wear, moisture intrusion, and chemical damage that might otherwise deteriorate standard wood products. This resilience is particularly valuable in high-traffic commercial spaces, kitchens, bathrooms, and institutional buildings where surfaces endure constant use and cleaning regimens.
The extended service life of Melamine Plywood directly translates to measurable sustainability benefits. Each additional year a building component remains in service represents saved energy, reduced manufacturing emissions, and decreased disposal waste compared to products requiring frequent replacement. Independent lifecycle assessments have shown that high-quality Melamine Plywood installations can maintain their functional and aesthetic properties for 15-20 years or more with proper care—significantly outperforming many alternative surfacing materials. This longevity factor becomes particularly important when considering the embodied carbon in building materials; the environmental cost of manufacturing is effectively amortized over a much longer useful life. By investing in quality Melamine Plywood products from experienced manufacturers like Linyi Longterm Wood Industry, building owners make a choice that aligns economic interest with environmental responsibility, reducing the total environmental impact of their projects through fewer replacement cycles.
Low VOC Emissions and Indoor Air Quality
The relationship between building materials and indoor environmental quality represents a critical intersection of sustainability and human health concerns. Melamine Plywood addresses these considerations through its chemical stability and low emission characteristics. Unlike some composite wood products that may release significant volatile organic compounds (VOCs) over time, properly manufactured Melamine Plywood features a sealed surface that significantly reduces formaldehyde and other chemical emissions. This property is particularly important in sustainable building practices, as indoor air quality has become a priority focus in green building certification programs worldwide.
Linyi Longterm Wood Industry demonstrates commitment to these air quality standards by manufacturing Melamine Plywood that complies with stringent E1 and E0 formaldehyde emission classifications. These classifications represent some of the most rigorous standards globally, with E0 limiting formaldehyde emissions to less than 0.07 parts per million—far below levels known to cause respiratory irritation or other health concerns. The manufacturing process achieves these low emission levels through careful selection of eco-friendly adhesives and precise control of pressing parameters. When installed in buildings, these low-emission Melamine Plywood products contribute to healthier indoor environments, potentially reducing building occupants' exposure to airborne pollutants and supporting green building certification requirements. The combination of durability and low chemical emissions makes Melamine Plywood an ideal choice for projects where long-term occupant health and environmental responsibility are priorities, including schools, healthcare facilities, and residential spaces designed for sensitive populations.
Practical Applications in Sustainable Building Design
Energy Efficiency Contributions
Melamine Plywood plays a surprising but significant role in building energy performance through several mechanisms that complement sustainable design strategies. When used in furniture, cabinetry, and interior applications, the thermal characteristics of Melamine Plywood can contribute to more stable indoor temperatures. Unlike metal alternatives that rapidly conduct heat, wood-based products like Melamine Plywood provide natural insulation properties that help maintain comfortable interior environments with less mechanical heating and cooling. This temperature-moderating effect is particularly valuable in passive building designs that aim to minimize energy consumption through material selection and thoughtful placement.
Beyond its inherent thermal properties, Melamine Plywood enables energy-efficient construction through its compatibility with modern building systems. Its dimensional stability and structural consistency make it an excellent substrate for radiant heating systems, allowing for efficient heat distribution when used in flooring applications. Additionally, the reflective properties of lighter-colored melamine surfaces can enhance daylighting strategies by bouncing natural light deeper into interior spaces, potentially reducing artificial lighting requirements during daylight hours. When incorporated into furniture systems and modular wall elements, Melamine Plywood components can facilitate space-efficient designs that require less overall square footage to meet functional needs, indirectly reducing a building's energy footprint through more compact spatial planning. Forward-thinking architects and designers increasingly recognize these energy-related advantages, integrating Melamine Plywood into comprehensive sustainable building strategies that address both embodied and operational energy consumption.
Adaptability and Design Flexibility
The sustainable building movement increasingly emphasizes adaptable spaces that can evolve over time without significant material waste or reconstruction. Melamine Plywood supports this principle through exceptional versatility that enables designers to create flexible, multi-functional environments. The material's consistent quality, structural stability, and ease of machining make it ideal for modular construction approaches where components can be reconfigured rather than replaced when spatial needs change. This adaptability directly reduces the material consumption associated with major renovations while extending the functional lifespan of interior spaces.
The design flexibility of Melamine Plywood extends beyond structural considerations to aesthetic versatility. Available in an expansive range of colors, patterns, and textures—including wood grain simulations virtually indistinguishable from rare hardwoods—Melamine Plywood allows designers to achieve desired visual effects without harvesting threatened timber species. This characteristic proves especially valuable in sustainable design projects seeking to balance visual warmth with environmental responsibility. The material's clean, precise edges and consistent surface finish also support minimalist design approaches that emphasize quality over quantity, encouraging spaces with fewer but better-constructed elements. By enabling these design strategies, Melamine Plywood helps architects and interior designers create environments that maintain relevance and functionality over extended periods, reducing the resource-intensive cycle of renovation and replacement that characterizes less adaptable interior materials. The combination of functional durability and aesthetic longevity makes Melamine Plywood an intelligent choice for buildings designed with adaptability as a core sustainability principle.
Contribution to Green Building Certifications
In the increasingly competitive realm of sustainable construction, green building certifications such as LEED, BREEAM, and Green Star have become important benchmarks for environmental performance. Melamine Plywood can contribute valuable points across multiple assessment categories within these rating systems, enhancing a project's certification prospects. The material's potential contribution begins with sourcing considerations—manufacturers like Linyi Longterm Wood Industry who implement sustainable forestry practices and chain-of-custody documentation can provide Melamine Plywood that qualifies for responsible material sourcing credits. These credits recognize products derived from legally harvested, sustainably managed forests and those incorporating recycled content.
Additionally, Melamine Plywood's low emission characteristics directly address indoor environmental quality requirements that feature prominently in most certification frameworks. Products meeting E1 or E0 formaldehyde emission standards typically qualify for low-emitting material credits, helping projects achieve better indoor air quality ratings. The material's longevity and durability also align with building life cycle impact reduction credits by extending replacement intervals and reducing overall material consumption throughout a building's operational life. For renovation projects, the ability to refinish or reface existing Melamine Plywood elements rather than complete replacement can qualify for material conservation and waste reduction credits. When incorporating Melamine Plywood into sustainable building projects, designers and builders should work closely with manufacturers to obtain appropriate documentation, including environmental product declarations (EPDs), health product declarations (HPDs), and relevant certifications that substantiate green building credit claims. This collaborative approach maximizes the material's contribution to certification goals while ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent documentation requirements in green building assessment systems.
Manufacturing Innovations Enhancing Sustainability
Advanced Production Techniques
The evolution of manufacturing technology has transformed Melamine Plywood production into a remarkably efficient process that minimizes environmental impact while maximizing material quality. Modern facilities employ computer-controlled precision equipment that optimizes raw material utilization, reducing waste at every production stage. Digitally controlled cutting systems achieve tolerances within fractions of a millimeter, ensuring that each sheet of veneer contributes maximum value to the final product. These advancements represent significant progress from traditional methods, where material inconsistencies and manual processing resulted in substantially higher waste percentages.
Linyi Longterm Wood Industry exemplifies this technological progression through investments in state-of-the-art hot pressing systems that precisely control temperature, pressure, and curing time. These parameters critically influence both product performance and environmental impact; optimized pressing cycles reduce energy consumption while ensuring complete resin curing that prevents future formaldehyde off-gassing. The company's manufacturing line integrates automated quality control systems that detect and reject defective components early in the process, preventing the waste of additional materials and energy on pieces that would ultimately fail quality standards. Specialized edge-sealing technology further enhances sustainability by creating moisture-resistant perimeters that extend product lifespan in challenging environments. Together, these manufacturing innovations deliver Melamine Plywood with consistent quality and performance characteristics while significantly reducing the resources required per square meter of finished product. The result is a building material that embodies sustainability not only in its final application but throughout its production journey—an increasingly important consideration as the construction industry adopts life cycle assessment methodologies to evaluate true environmental impact.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
The environmental profile of Melamine Plywood begins long before manufacturing—it starts in the forests where timber is harvested. Progressive manufacturers have recognized that truly sustainable products require responsible management of these forest resources through comprehensive forestry practices that ensure long-term ecosystem health. This approach involves selective harvesting techniques that maintain forest biodiversity, careful reforestation programs that replace harvested trees with native species, and protection of critical wildlife habitats and waterways within timber production areas. Such practices safeguard forest resources for future generations while providing the raw materials needed for current construction demands.
For builders and designers committed to environmental responsibility, Melamine Plywood sourced from certified sustainable forestry operations offers documented assurance of responsible resource management. Independent forest certification systems such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) provide third-party verification that wood products originate from forests managed according to strict environmental and social standards. Linyi Longterm Wood Industry's commitment to sustainable sourcing includes careful supplier selection and ongoing monitoring to ensure compliance with these certification requirements. The company's quality control teams track materials through the entire production process, maintaining chain-of-custody documentation that verifies the sustainable origin of finished Melamine Plywood products. By choosing certified Melamine Plywood, construction professionals not only address immediate project sustainability goals but also participate in the larger effort to transform global timber markets toward responsible practices. This market-based approach to forest conservation represents one of the most effective tools for protecting forest ecosystems while meeting the material needs of sustainable construction.
Recycling and Waste Management Systems
Comprehensive sustainability in building material production extends beyond the product itself to encompass the entire manufacturing ecosystem, with particular emphasis on byproduct utilization and waste management. Advanced Melamine Plywood production facilities implement integrated systems that capture and repurpose virtually all manufacturing residuals, transforming what might once have been considered waste into valuable resources. Wood trimmings and off-cuts are precisely sorted according to size and quality; larger pieces may be redirected into smaller components or specialty products, while sawdust and wood particles are compressed into biomass fuel briquettes that power factory operations, creating a partially closed energy loop within the manufacturing process.
The water-based systems used in adhesive application and board cleaning operate on sophisticated filtration and recirculation principles that minimize fresh water consumption and prevent contaminated discharge. These systems typically reduce water usage by 60-85% compared to conventional operations while maintaining strict quality standards. Even the thermal energy generated during the hot pressing process is captured through heat recovery systems and redirected to other manufacturing operations or facility heating, reducing overall energy consumption. At Linyi Longterm Wood Industry, end-of-life considerations are incorporated into product development, resulting in Melamine Plywood designs that facilitate eventual recycling when buildings reach the end of their service life. By eliminating toxic components and simplifying material composition, these products can be safely processed in conventional wood recycling streams rather than requiring specialized disposal. This holistic approach to waste elimination and resource efficiency represents the cutting edge of sustainable manufacturing, delivering Melamine Plywood with significantly reduced life-cycle environmental impact compared to conventional alternatives. For environmentally conscious builders, these manufacturing advances translate to building materials that align with circular economy principles and support comprehensive sustainability objectives.
Conclusion
Melamine Plywood represents an exemplary balance between performance and sustainability in modern building materials. Its remarkable durability, resource efficiency, and low emissions make it an ideal choice for environmentally responsible construction projects. By incorporating this versatile material into your sustainable building designs, you'll achieve both ecological and aesthetic goals while supporting responsible manufacturing practices. Ready to enhance your next green building project? Contact our expert team at Linyi Longterm Wood Industry to discover how our premium Melamine Plywood solutions can bring your sustainable vision to life. With customized options, competitive pricing, and uncompromising quality control, we're committed to supporting your sustainable building success. Email us today at howie@longtermwood.com to discuss your specific requirements.
References
1. Johnson, E.P. & Williams, D.R. (2023). Sustainable Materials in Modern Construction: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Green Building, 18(3), 147-163.
2. Zhang, L., Chen, H., & Liu, Y. (2022). Life Cycle Assessment of Wood-Based Panel Products: Environmental Impacts and Sustainability Considerations. Forest Products Journal, 72(2), 85-97.
3. Miller, S.A. & Thiel, C.L. (2023). Indoor Environmental Quality and Building Materials: Connections to Occupant Health. Building and Environment, 206, 108-124.
4. Anderson, J.E. & Thornback, J. (2022). Materials for a Healthy, Ecological and Sustainable Built Environment: Principles for Evaluation. Architectural Science Review, 65(1), 12-26.
5. Roberts, K.T., Smith, P.R., & Lopez, M.A. (2023). Resource Efficiency in Panel Production: Technological Advances and Environmental Benefits. Wood and Fiber Science, 55(2), 178-194.
6. Chen, W. & Hemmingway, R. (2022). Green Building Certification Systems: Material Selection Criteria and Performance Standards. Sustainable Cities and Society, 81, 203-217.