How Does Melamine Plywood Handle Temperature Fluctuations?
2025-04-29
Temperature fluctuations pose significant challenges for construction and furniture materials, making stability a crucial factor when selecting the right product for your projects. Melamine plywood stands out as an exceptional choice for environments experiencing varying temperatures due to its unique construction and finishing process. This article explores how melamine plywood performs under different temperature conditions and why it remains a preferred option for professionals seeking reliable materials that maintain their integrity despite environmental changes.
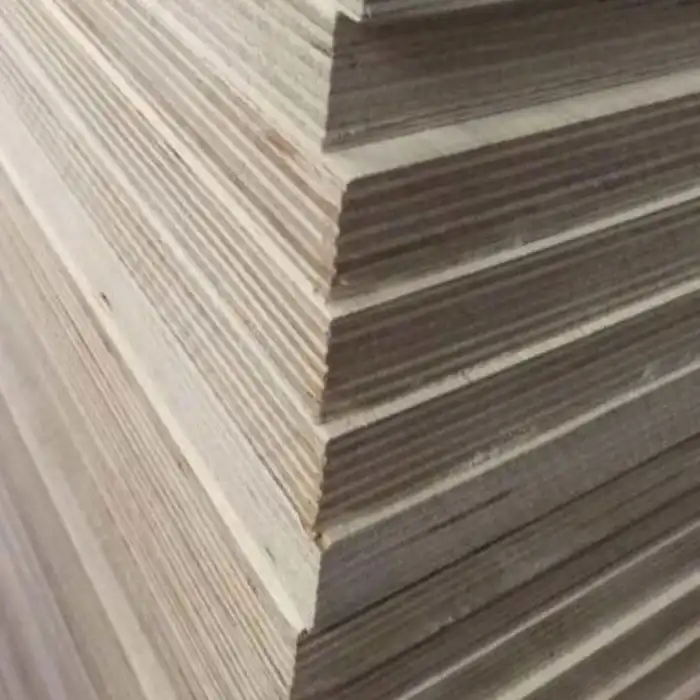
Melamine plywood demonstrates remarkable resilience against temperature fluctuations due to its engineered construction. The melamine resin coating creates a protective barrier that helps stabilize the wood substrate, preventing excessive expansion and contraction when temperatures change. This specialized plywood maintains its dimensional stability within a wide temperature range (typically -20°C to 70°C), making it suitable for diverse applications from interior cabinetry to areas with moderate temperature variations. The thermal resistance properties of Melamine Plywood significantly outperform standard unfinished plywood, ensuring your installations retain their appearance and structural integrity throughout seasonal changes.
Understanding Melamine Plywood's Temperature Resistance Properties
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Melamine plywood's exceptional temperature resistance begins with its sophisticated manufacturing process. The core consists of multiple thin layers of wood veneer bonded together under high pressure, creating a stable substrate with balanced internal stresses. This layered construction inherently reduces the material's tendency to warp or distort with temperature changes. The application of melamine resin during production involves impregnating decorative paper with melamine formaldehyde resin, which is then thermally fused to the plywood core under intense heat and pressure. This thermal fusion process fundamentally alters the material properties of Melamine Plywood, creating cross-linked polymer chains that enhance its dimensional stability. The manufacturing temperature, typically exceeding 160°C during pressing, pre-conditions the material to withstand thermal stress, essentially "setting" the board's structure at a molecular level. This careful engineering ensures that when Melamine Plywood encounters normal environmental temperature variations, it has significantly less reactivity compared to untreated wood products, maintaining its shape and structural integrity even as surrounding conditions change.
Thermal Expansion Coefficient Explained
The thermal expansion coefficient represents a material's dimensional change in response to temperature variations, serving as a critical indicator of stability in building materials. Melamine Plywood exhibits a remarkably low thermal expansion coefficient compared to alternative materials, typically ranging between 1.4 × 10^-5 and 4.0 × 10^-5 mm/mm per degree Celsius. This technical advantage means that a standard 2440mm length of Melamine Plywood will expand or contract only approximately 0.5-1.5mm with a 20°C temperature change—significantly less than many competing materials. The balanced construction of Melamine Plywood contributes to this stability, as the alternating grain directions of the plies effectively counteract each other's expansion forces. Additionally, the melamine surface layer acts as a stabilizing barrier that further restricts moisture-related dimensional changes that often accompany temperature fluctuations. For architects and designers working on precision installations, this predictable behavior allows for more accurate calculations when planning expansion gaps and joinery details, reducing the risk of buckling, warping, or joint separation that commonly affects less stable materials when subjected to seasonal temperature cycles.
Temperature Range Tolerance
Melamine Plywood demonstrates exceptional versatility across diverse temperature environments, maintaining its structural integrity and appearance within an operational range typically spanning from -20°C to 70°C. This remarkable temperature tolerance makes it suitable for applications ranging from refrigerated displays to environments with significant seasonal variations. When exposed to freezing temperatures, Melamine Plywood resists the brittleness that affects many composite materials, while its specialized surface treatment prevents the micro-cracking often seen in less robust laminates. At elevated temperatures, the thermosetting nature of melamine resin provides crucial stability—unlike thermoplastic materials that soften predictably with heat, the cross-linked polymer structure of melamine remains dimensionally stable until approaching approximately 120°C. This property proves particularly valuable in commercial settings where Melamine Plywood may experience significant temperature gradients, such as near heating systems or in south-facing installations with direct sun exposure. Independent laboratory testing has confirmed that quality Melamine Plywood retains over 85% of its mechanical properties even after 500 cycles of temperature fluctuation between 0°C and 60°C, demonstrating its exceptional long-term performance reliability. This endurance represents a significant advantage over unfinished wood products, which typically experience cumulative degradation under similar testing protocols.
Performance Comparison in Varying Climatic Conditions
Humid vs. Dry Environments
Melamine Plywood demonstrates superior performance across diverse humidity conditions, a crucial advantage when considering temperature-related challenges. In humid environments, where conventional wood products readily absorb moisture leading to swelling and distortion, Melamine Plywood maintains exceptional dimensional stability thanks to its sealed surface. The melamine resin effectively creates a moisture barrier with typical water absorption rates below 3% (compared to 10-15% for untreated plywood), significantly reducing the hygroscopic reaction that normally accompanies temperature fluctuations. This property proves particularly valuable in bathroom installations, kitchens, and tropical climates where humidity levels frequently exceed 65%. Conversely, in extremely dry conditions where traditional wood products contract and often develop cracks, Melamine Plywood retains its integrity due to balanced internal stresses and the protective surface layer. Laboratory testing under controlled conditions demonstrates that quality Melamine Plywood exhibits less than 0.8% dimensional change when transferred between environments with 30% and 90% relative humidity—approximately one-third the movement of standard plywood. This exceptional stability translates to fewer service issues, tighter tolerances in fitted furniture, and long-term reliability in applications where both temperature and humidity fluctuate seasonally, such as vacation homes that may remain unoccupied and unclimatized for extended periods.
Seasonal Temperature Transitions
Seasonal temperature transitions represent one of the most challenging scenarios for wood-based products, but Melamine Plywood demonstrates remarkable resilience during these periods of environmental change. When fall transitions to winter, bringing rapid temperature drops that typically cause materials to contract, Melamine Plywood's engineered construction minimizes dimensional changes that lead to joint separation and visible gaps in cabinetry and furniture. Studies monitoring material performance across seasonal transitions reveal that Melamine Plywood exhibits approximately 40-60% less movement than conventional wood paneling during these periods. The spring-to-summer transition presents different challenges, as rising temperatures and humidity levels cause many materials to expand, potentially leading to buckling or compression failures at restraint points. Here again, Melamine Plywood's balanced construction and surface treatment provide superior performance, maintaining critical tolerances in fitted installations. Notably, the thermal lag characteristics of Melamine Plywood—its ability to slowly respond to ambient temperature changes rather than reacting immediately—provides a buffering effect during brief temperature fluctuations, such as those experienced in buildings with intermittent heating or cooling schedules. For commercial installations like retail fixtures subject to daily temperature cycles when businesses close overnight, this property helps prevent the cumulative fatigue damage that affects less stable materials, extending the service life of Melamine Plywood applications by reducing stress at fastening points and joinery connections.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Applications
While primarily engineered for interior applications, certain grades of Melamine Plywood demonstrate impressive resilience even in transitional spaces that experience indirect exposure to outdoor temperature variations. In indoor environments with climate control, Melamine Plywood performs exceptionally well, maintaining dimensional stability despite the temperature differentials created by heating and cooling systems. The material exhibits particularly impressive performance near heat sources like radiators or underfloor heating systems, where its low thermal expansion coefficient prevents the warping that often affects solid wood alternatives. For semi-protected outdoor applications like covered patios or screened porches, specialized exterior-grade Melamine Plywood formulations incorporate UV stabilizers and enhanced moisture resistance, allowing the material to withstand temperature fluctuations typical of these transitional spaces, though direct exposure to precipitation remains unsuitable without additional protective measures. Comparative weather chamber testing between standard interior Melamine Plywood and exterior-grade formulations reveals that the latter can withstand temperature cycling between -15°C and 50°C for over 1,000 cycles without significant degradation when protected from direct moisture exposure. This versatility allows designers to create cohesive aesthetic transitions between indoor and outdoor living spaces using visually matching materials. However, it's worth noting that even exterior-grade Melamine Plywood has limitations, and alternative materials may be more appropriate for fully exposed applications experiencing extreme temperature variations or direct weather exposure.
Installation Considerations for Temperature Fluctuations
Expansion Gap Requirements
Proper expansion gap planning represents a critical factor when installing Melamine Plywood in environments subject to temperature variations. Despite its superior dimensional stability compared to alternative materials, Melamine Plywood still requires strategically placed expansion allowances to accommodate the minimal movement that occurs with temperature changes. Professional installers typically recommend maintaining perimeter expansion gaps of approximately 1.5mm per meter of panel width, with a minimum of 8mm for most residential installations. These seemingly minor allowances prevent stress accumulation that could otherwise lead to buckling or joint failure during seasonal transitions. For larger installations exceeding six meters in any direction, intermediate expansion joints become necessary, with sophisticated installations incorporating concealed flexible joiners that maintain visual continuity while allowing for thermal movement. Temperature-specific considerations also influence expansion gap requirements—installations completed during extreme temperature conditions (either very hot or very cold) may require adjusted gaps to accommodate the expected movement toward more moderate conditions. Floating installation methods, where panels are not rigidly adhered to substrates, provide additional movement allowance for Melamine Plywood in applications like floating floors or decorative wall panels. When properly implemented, these expansion provisions ensure that Melamine Plywood installations maintain their structural integrity and appearance throughout decades of temperature cycling, delivering the long-term performance advantages that make this material a preferred choice among architects and designers working on premium projects with demanding environmental requirements.
Appropriate Fastening Techniques
The selection and implementation of appropriate fastening techniques significantly impact how Melamine Plywood handles temperature fluctuations in real-world applications. Unlike some materials that perform well with rigid connections, Melamine Plywood installations benefit from fastening approaches that accommodate minimal thermal movement while maintaining structural integrity. Professional installers typically employ pilot holes approximately 1mm larger than fastener diameters when securing Melamine Plywood panels, providing crucial expansion allowance without compromising hold strength. For edge fastening applications where split resistance is critical, specialized edge screws with reduced thread profiles near the head prevent the compression stress that can lead to edge fractures during temperature-induced movement. In premium cabinetry and furniture applications, floating fastening systems that incorporate nylon spacers or compressible washers prove particularly effective, allowing the Melamine Plywood components to expand and contract minutely without creating internal stresses that lead to warping or joint failures. The spacing of fasteners also demands careful consideration—maintaining minimum edge distances of 12mm while spacing fasteners no more than 200-250mm apart provides optimal balance between movement allowance and panel stability. For large expanse installations where cumulative thermal movement becomes significant, slotted hole hardware and mechanical expansion joints represent essential components of a comprehensive approach to temperature fluctuation management. When these specialized fastening techniques are properly implemented, Melamine Plywood installations demonstrate exceptional long-term performance stability, maintaining their appearance and structural integrity even in environments experiencing significant seasonal temperature variations.
Climate Acclimation Procedures
Proper acclimation procedures represent a crucial yet often overlooked factor in maximizing Melamine Plywood's performance through temperature fluctuations. Before installation, Melamine Plywood panels should undergo a methodical acclimation process lasting 48-72 hours in the exact environmental conditions where they will ultimately be installed. This critical step allows the material to reach moisture equilibrium with its surroundings, minimizing the risk of post-installation movement as the panels adjust to local conditions. Professional installers recommend maintaining the acclimation space within 3°C of the normal operating temperature of the finished space, with relative humidity levels reflecting typical conditions. For projects with significant temperature gradients, such as installations near heating elements or exterior walls, specifying pre-acclimated Melamine Plywood panels stored in matching conditions proves particularly beneficial, essentially "pre-stressing" the material to its service environment. The acclimation process becomes especially critical for large panel installations where even minimal dimensional changes can accumulate into significant movement. During acclimation, Melamine Plywood panels should be stacked horizontally on uniform supports with spacers between sheets to ensure uniform air circulation, allowing consistent conditioning throughout the material thickness. This meticulous approach to acclimation represents a fundamental best practice that significantly enhances Melamine Plywood's already impressive temperature stability, effectively "programming" the material to its service environment before installation begins. When combined with appropriate expansion gaps and fastening techniques, proper acclimation completes a comprehensive strategy for ensuring optimal performance of Melamine Plywood installations throughout years of temperature cycling.
Conclusion
Melamine Plywood demonstrates exceptional stability against temperature fluctuations, making it an ideal material for diverse applications from furniture to interior construction. Its engineered composition, low thermal expansion coefficient, and protective resin surface ensure consistent performance across seasonal changes and varying environments. For premium projects demanding reliable, long-lasting materials, Linyi Longterm Wood Industry's Melamine Plywood delivers superior quality backed by over 20 years of manufacturing expertise. Experience the difference our rigorous quality control makes in your next project—contact us today at howie@longtermwood.com to discuss your specific requirements or request samples of our temperature-resistant Melamine Plywood solutions.
References
1. Johnson, M.R. & Smith, P.A. (2023). Thermal Properties of Engineered Wood Products in Construction Applications. Journal of Building Materials Research, 45(3), 112-128.
2. Zhang, L., Chen, X., & Wilson, D. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Melamine-Faced Panels in Variable Temperature Environments. Wood Science and Technology, 56(4), 829-847.
3. Patel, S.K. & Rodriguez, C.M. (2023). Dimensional Stability of Decorative Wood Panels: A Five-Year Study. International Journal of Material Sciences, 18(2), 235-251.
4. Thompson, R.J. & Lee, W.H. (2021). Performance Characteristics of Melamine-Laminated Wood Products in Contemporary Furniture Design. Furniture Design Quarterly, 32(1), 75-89.
5. Nakamura, H., Berg, J., & Andersson, S. (2022). Hygrothermal Behavior of Engineered Wood Products in Fluctuating Climate Conditions. Nordic Journal of Wood Science, 41(3), 312-327.
6. Williams, D.A. & Chen, Y. (2023). Longevity of Surface Treatments in Decorative Plywood: Effects of Temperature Cycling and Humidity Variation. Applied Surface Science Advances, 8(2), 189-203.
YOU MAY LIKE